Medication reconciliation
Clinicians may not be aware of the term 'medication reconciliation' or may have differing understandings of the term.
Medication reconciliation (Med Rec) is a formal process of obtaining, verifying and documenting an accurate list of a patient's current medications on admission and comparing this list to the admission, transfer, and/or discharge medication orders to identify and resolve discrepancies. At the end of the episode of care, the verified information is transferred to the patient and next care provider.
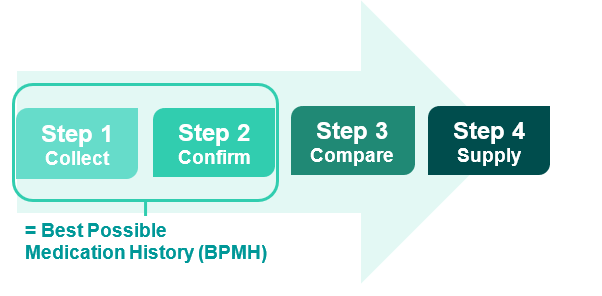
- Collect information to compile a list of each patient's current medications (each medication must be clearly identified and have clear directions i.e. name, dose, frequency).
- Confirm the accuracy of the information collected to achieve a BPMH.
- Compare the BPMH with prescribed medicines at every transfer of care; identifying and rectifying any discrepancies.
- Supply accurate medicines information to the patient and next care provider.
The BPMH is an important foundation of Med Rec - collecting and confirming the patient's current medications. This forms the basis of medication treatment decisions. Visit the BPMH page for more information.
Med Rec and Medication Review are distinct but interrelated processes.
Med Rec involves ensuring accurate and complete medicines information is communicated at all transfers of care. Med Rec will often result in identification of medication discrepancies (e.g. differences between the documented medication history and the admission medication orders) which may be intentional or unintentional.
Medication review involves an evaluation of a patient’s medicines with the aim of optimising the quality use of medicines. A medication review will often result in the identification of actual or potential medication-related problems and recommendations to optimise medicines use. Visit the Medication Review page for more information.
Framework for Med Rec
The Med Rec framework assists services in formalising Med Rec processes and outlines how these will benefit patients as well as what action is required to achieve these benefits.
Why is Med Rec important?
Up to 50% of medication errors occur at transfers of care. Unintentional changes to patients’ medicines at transfers of care can result in considerable harm and have been linked to poorer health outcomes, increased hospital readmissions and mortality.1, 2 Medication errors and adverse drug events can be prevented by having a formalised Med Rec process.3
The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care's (ACSQHC) National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards (second edition) require health service organisations to have processes whereby:
- Clinicians take a best possible medication history, which is documented in the healthcare record on presentation or as early as possible in the episode of care.
- Clinicians review a patient’s current medication orders against their best possible medication history and the documented treatment plan and reconcile any discrepancies on presentation and at transitions of care.
- Gillespie, U., A. Alassaad, et al. (2009). A comprehensive pharmacist intervention to reduce morbidity in patients 80 years or older: A randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 169(9): 894-900.
- Cornish PL, Knowles SR et. al. (2005). Unintentional medication discrepancies at the time of hospital admission. Arch Intern Med 165: 424-429.
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. (2017). National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards Guide for Hospitals. Sydney: ACSQHC.
How can you improve your local Med Rec process?
A clearly defined Med Rec process can assist in medication reconciliation being completed for every patient.
The Med Rec toolkit – making improvements provides a step by step guide and resources that can be adopted locally.
The CEC Med Rec local operating procedure assists health services to define these processes.
Med Rec relies heavily on multidisciplinary teamwork and effective communication. This CEC guide assists health services in determining roles, responsibilities and documenting requirements of Med Rec.
It is important to consider the 'who', 'where' and 'how' to:
- document medication histories/changes/interventions/plans accessible to all clinicians
- communicate and resolve medication changes/interventions/discrepancies
- generate and supply medicines information including patient friendly information at the point of transfer/ discharge. Find out more about the Cerner eMR Patient Friendly Medication List solution.
- measure and report on accurate Med Rec data.
How can you get involved and learn more?
Below is a list of Med Rec resources available for you to adapt to suit your local needs.
Join the group to share learnings to improve Med Rec.
This toolkit provides information, resources and quality improvement (QI) tools for managers and clinicians to improve Med Rec in health services.
Visit the education and training page for extensive Med Rec resources.